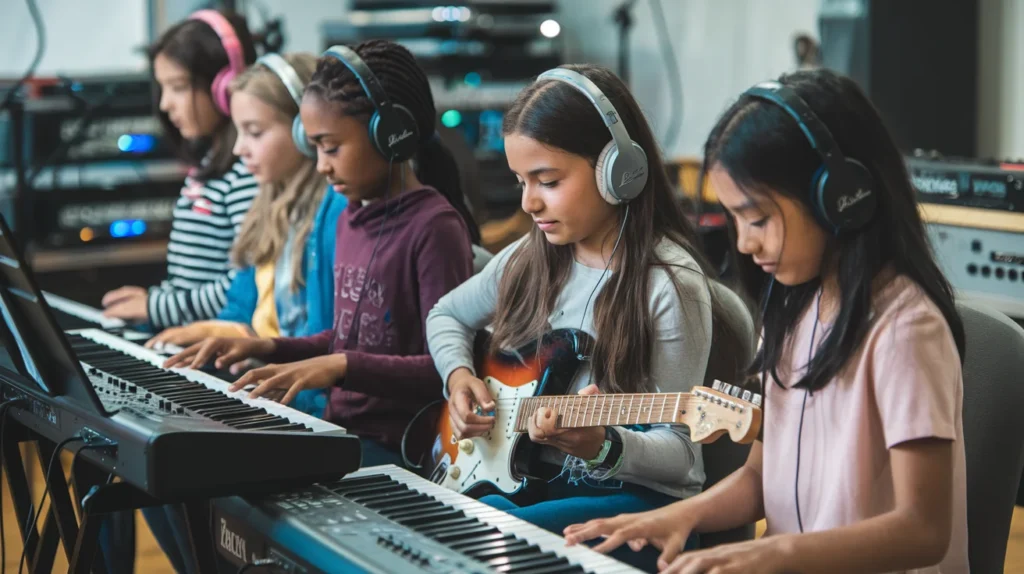
Music has evolved drastically over the decades, not only in style but also in the way it is produced. What is music technology? Simply put, it is the application of tools, software, and equipment to create, record, and enhance music.
From traditional instruments to digital sound systems, music technology bridges creativity with technical innovation. Moreover, musicians today rely on advanced devices and software, which make composing and producing music more accessible and efficient. As a result, the boundaries of musical expression continue to expand, allowing artists to explore new sounds and techniques.
Understanding what music technology is helps beginners and professionals alike grasp how music is made, recorded, and shared globally. This knowledge is essential for anyone aiming to thrive in the modern music industry.
The Evolution of Music Technology
The history of music technology spans several centuries, reflecting humanity’s constant pursuit of new ways to create and enhance sound. Early innovations were largely mechanical, such as the piano, organ, and harpsichord, which allowed musicians to produce more complex and expressive compositions than ever before.
These instruments laid the foundation for musical experimentation, influencing classical compositions and performances throughout history. Over time, the development of recording devices like the phonograph and tape recorder further changed the way music was shared, making it possible to preserve and reproduce sound with unprecedented accuracy.
Today, modern music technology has expanded even further to include computers, digital audio workstations (DAWs), MIDI controllers, and virtual instruments. These tools not only allow for precise sound manipulation but also make collaboration easier, enabling artists across the globe to create, record, and produce music in innovative ways that continue to redefine the industry.
Key Components of Music Technology

Music technology relies on a combination of software, hardware, and digital tools that work together to streamline music creation, recording, and production. These components allow musicians to experiment with sounds, enhance compositions, and achieve professional-quality output efficiently. Some of the key tools include:
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
Digital Audio Workstations, or DAWs, are software platforms like Ableton Live, FL Studio, and Logic Pro that serve as the central hub for music creation. They allow musicians and producers to compose, record, edit, and mix tracks all within a single environment.
DAWs provide a wide range of tools, including virtual instruments, audio effects, and multi-track recording capabilities, making it possible to produce professional-quality music entirely digitally.
MIDI Controllers
MIDI Controllers are devices that send digital signals to virtual instruments, enabling musicians to perform electronic sounds just like traditional instruments. These controllers often come in the form of keyboards, drum pads, or other input devices, giving artists tactile control over pitch, velocity, and modulation.
Audio Interfaces
Audio interfaces are hardware devices that connect microphones, instruments, and other audio sources to a computer for high-quality recording. They convert analog signals into digital data that can be processed by music production software.
Audio interfaces are essential for capturing clean, professional-grade sound and often include preamps, multiple input/output channels, and low-latency monitoring for precise production.
Synthesizers and Samplers
Synthesizers and samplers are tools designed to create, manipulate, and reproduce unique sounds. It generates electronic tones and textures, while samplers allow musicians to record, modify, and replay real-world sounds digitally.
These instruments expand creative possibilities, enabling producers to craft distinctive audio elements that define modern music genres.
How Music Technology Impacts Modern Music
Music technology has profoundly transformed the modern music industry, enabling artists and producers to explore new creative possibilities while improving production quality. It allows musicians to design innovative sounds, experiment with digital effects, and collaborate seamlessly across the globe.
The impact of these advancements is visible in the way music is composed, recorded, and shared today, making what is music technology a driving force behind modern musical innovation.
Key ways music technology influences music include:
- Musicians can create complex arrangements and layered compositions without needing a full orchestra.
- Producers can experiment with sound textures, effects, and digital instruments to craft unique audio experiences.
- Online platforms and cloud-based tools allow for real-time collaboration between artists from different parts of the world.
Through these tools, music technology not only simplifies production but also expands creative freedom, shaping the soundscape of today and the future.
Types of Music Technology Tools
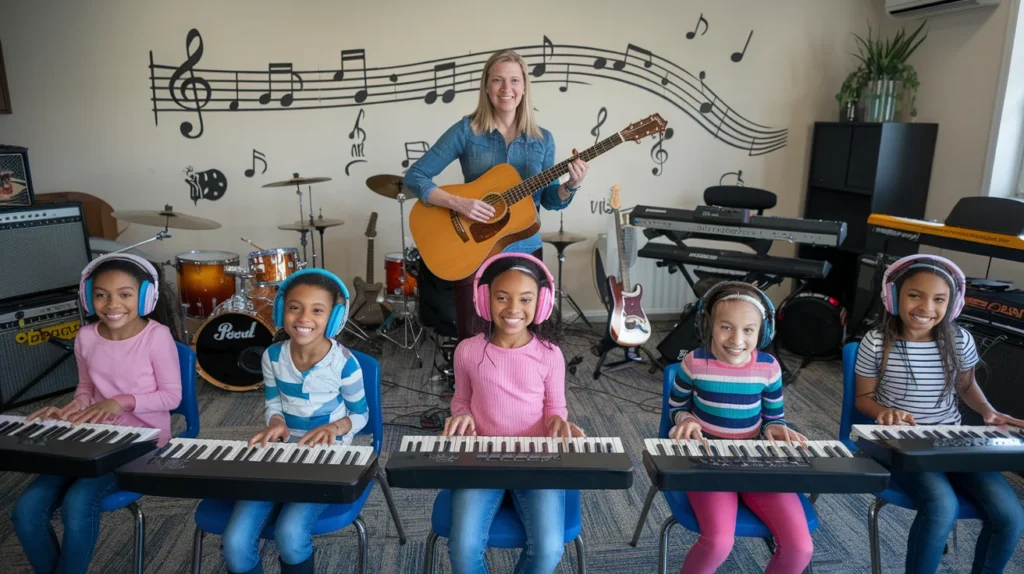

Musicians and producers rely on a variety of tools to create, manipulate, and refine music, ranging from software applications to specialized hardware. These tools are essential for producing professional-quality tracks, experimenting with sound, and streamlining the music creation process. Understanding their functions helps artists maximize creativity and efficiency.
Audio Editing Software
Audio editing software, such as Pro Tools, Logic Pro, and Audacity, allows musicians to record, edit, and mix audio with precision. These programs provide multi-track capabilities and various tools to refine sound quality. They are essential for producing professional-grade music efficiently.
Virtual Instruments
Virtual instruments replicate real-world sounds like pianos, drums, and orchestral instruments using software. They allow musicians to compose and perform digitally without needing physical instruments. This flexibility expands creative possibilities for music production.
Recording Equipment
Recording equipment includes high-quality microphones, audio interfaces, and headphones that capture sound accurately. These tools ensure clear, professional recordings for both studio and live environments. Proper equipment is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity.
Loop Libraries
Loop libraries are collections of pre-recorded sounds that musicians can use to create rhythms and melodies. They save time and inspire creativity during the composition process. Loops can be easily integrated into digital audio workstations.
Effect Plugins
Effect plugins, such as reverb, delay, compression, and distortion, creatively enhance or modify audio. They allow producers to shape the sound, add depth, and create unique audio textures. Plugins are a vital part of modern music production.
Together, these tools make modern music production versatile, innovative, and accessible to both beginners and professional musicians.
Benefits of Music Technology
Music technology has revolutionized the way music is created, making the production process simpler and more efficient. Artists can now produce high-quality tracks independently, without the need for a full professional studio.
This accessibility allows musicians to experiment freely with sound, layering, and composition, resulting in innovative and unique musical pieces. By integrating digital tools, creators can explore experimental approaches that were previously difficult or impossible with traditional instruments alone.
This inclusivity has opened doors for new talent worldwide, enabling emerging artists to participate in the music industry without geographical or financial limitations. As a result, the modern music landscape has become more diverse, innovative, and accessible than ever before.
Challenges in Music Technology
Despite its numerous advantages, music technology comes with certain challenges that musicians and producers must navigate. Mastering digital tools requires time and effort, and balancing creativity with technical skills can be demanding. Additionally, high-quality equipment and software often involve significant costs, which can be a barrier for beginners or independent artists.
Key challenges in music technology include:
- Learning Curve: Mastering DAWs, MIDI controllers, and other tools can be overwhelming for beginners.
- Cost: Professional-grade equipment and software often require substantial investment.
- Over-Reliance on Technology: Excessive dependence on digital tools may compromise the authenticity of music.
- Maintaining Creativity: Artists must blend traditional musical skills with technological expertise to produce compelling compositions.
- Constant Updates: Software and tools frequently update, requiring continuous learning and adaptation.
These challenges highlight the need for a balanced approach, ensuring that technology enhances creativity without overshadowing the artist’s musical vision.
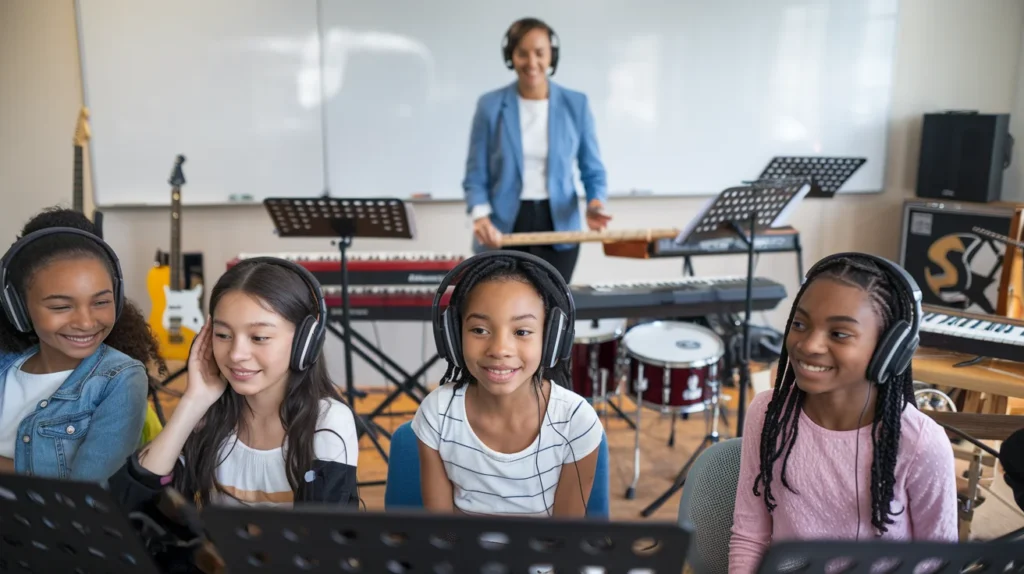
Music Technology in Education
Education systems around the world are increasingly incorporating music technology to equip students with modern musical skills. Digital tools make learning interactive and practical, allowing students to experiment with sound, composition, and recording in real time.
By using software like digital audio workstations (DAWs) and virtual instruments, learners gain hands-on experience that bridges the gap between theory and practice, making the learning process engaging and effective.
By integrating these tools into the curriculum, schools and universities prepare students for careers in the evolving music industry, ensuring they are equipped with the knowledge and experience needed to thrive in a technology-driven musical landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding what music technology is essential for anyone interested in modern music production. It combines creativity, technical skills, and innovative tools to create, record, and enhance music efficiently. With the advancement of technology, from digital audio workstations to synthesizers and virtual instruments, music technology empowers artists to explore new sounds and production techniques.
As the music industry continues to evolve, embracing technology enables musicians to collaborate globally, experiment with innovative sounds, and reach a wider audience. By leveraging these tools, both beginners and professionals can unlock their full creative potential and shape the future of music.